Market volatility is a fundamental aspect of financial markets, representing the degree of variation in asset prices over time. It is often seen as a measure of risk, as it reflects how much and how quickly prices fluctuate in response to economic events, investor sentiment, and global uncertainties. While high volatility can create opportunities for traders to capitalize on price swings, it also increases risk and unpredictability. On the other hand, low volatility provides stability but may limit profit potential. Understanding market volatility is essential for traders and investors to develop effective strategies that align with changing market conditions. In this article, we will explore what market volatility is, how it is measured, its impact on different trading strategies, and how traders can navigate volatile markets to maximize returns while managing risk.
What is Market Volatility?
Market volatility refers to the rate at which asset prices fluctuate within a specific period. It is a key indicator of uncertainty and risk in financial markets, showing how drastically prices move up or down. High volatility signifies large and rapid price swings, often driven by economic data releases, geopolitical events, or shifts in investor sentiment. Conversely, low volatility indicates stable and gradual price movements, usually reflecting a more predictable market environment. While volatility can create opportunities for traders to profit from price fluctuations, it also increases the level of risk, making it essential for investors to understand and manage it effectively.
 Causes of Market Volatility
Causes of Market Volatility
Market volatility arises from various factors that influence price movements, often leading to rapid and unpredictable changes in asset values. These fluctuations can be triggered by economic conditions, investor sentiment, political events, or unexpected global crises. While some volatility is a normal part of market activity, extreme volatility can create both risks and opportunities for traders. By understanding what drives market volatility, investors can better navigate uncertain conditions and develop strategies to mitigate risk.
Key Causes of Market Volatility:
1. Economic Indicators
Reports on inflation, employment, gross domestic product (GDP) growth, and interest rate decisions significantly impact market sentiment. A higher-than-expected inflation rate, for instance, can lead to fears of monetary tightening, triggering sell-offs in the stock market.
2. Corporate Earnings Reports
The performance of major corporations directly affects stock prices. Positive earnings reports can boost investor confidence and drive stock prices higher, while disappointing results can lead to sharp declines.
3. Political and Geopolitical Events
Elections, policy shifts, trade wars, sanctions, and geopolitical tensions can create uncertainty in financial markets. For example, a sudden escalation in international conflicts or major regulatory changes can result in heightened volatility.
4. Investor Sentiment and Speculation
Fear and greed play a significant role in market movements. A surge in speculative trading, fueled by hype or fear-driven selling, can lead to sharp price fluctuations, often detached from fundamental market conditions.
5. Market Liquidity
Low liquidity means fewer buyers and sellers in the market, which can exaggerate price movements. In highly liquid markets, large trades have minimal impact, whereas in low-liquidity conditions, even small trades can cause substantial price swings.
6. Unexpected Global Events
Natural disasters, pandemics, financial crises, and major technological failures can shake market stability. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic caused extreme volatility as investors reacted to economic shutdowns and uncertainty about the future.
Types of Market Volatility
Market volatility can take different forms, depending on the factors driving price movements and how they are measured. Understanding these variations helps traders and investors make informed decisions based on market conditions. Volatility is not always a sign of instability; in some cases, it indicates healthy price fluctuations that create opportunities for profit. Below are the main types of market volatility that impact financial markets.
1. Historical Volatility
This refers to past price fluctuations of an asset over a specific period. It is calculated using statistical measures such as standard deviation to determine how much prices have varied in the past. Traders use historical volatility to assess risk and predict potential future movements.
2. Implied Volatility
Implied volatility (IV) is a forward-looking measure that estimates expected price fluctuations based on options pricing. A higher IV suggests that the market anticipates significant price swings, while a lower IV indicates stability. It is commonly used by options traders to determine potential risk and pricing strategies.
3. Realized Volatility
Also known as actual volatility, this measures how much an asset’s price has fluctuated in the past based on historical price data. It is different from implied volatility, which predicts future movements. Realized volatility is useful for evaluating how volatile an asset has been in a given time frame.
4. Intraday Volatility
This type of volatility focuses on price movements within a single trading session. Day traders and short-term investors closely monitor intraday volatility to capitalize on rapid price fluctuations. Stocks and assets with high intraday volatility present opportunities for quick profits but also carry higher risks.
5. Market-Wide Volatility
This occurs when the entire financial market experiences sharp fluctuations due to broader economic or geopolitical factors. Major events such as interest rate changes, inflation reports, or global crises can cause widespread volatility, affecting stocks, bonds, and commodities alike. The VIX (Volatility Index) is often used to gauge market-wide volatility levels.
 How Market Volatility Impacts Trading Strategies
How Market Volatility Impacts Trading Strategies
Market volatility plays a crucial role in shaping trading strategies, as price fluctuations directly impact risk, profit potential, and decision-making. In highly volatile markets, traders can capitalize on larger price swings, but they also face increased uncertainty and risk. Conversely, in low-volatility environments, price movements are more predictable, but profit opportunities may be limited. Traders must adapt their strategies based on market conditions to balance risk and reward effectively. Below are the key ways in which market volatility influences different trading strategies.
1. Day Trading Becomes More Profitable but Riskier
Day traders thrive in volatile markets because frequent price swings create multiple trading opportunities. However, higher volatility also increases the risk of sudden losses, requiring strict risk management strategies such as stop-loss orders and position sizing.
2. Swing Trading Gains from Larger Price Movements
Swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, benefiting from medium-term price fluctuations. In volatile markets, they can capture bigger price movements, but they must also be prepared for sudden reversals that can impact profits.
3. Long-Term Investing Faces Short-Term Uncertainty
Volatility can cause short-term price drops that may unsettle long-term investors. However, for those with a strong investment strategy, market dips can present buying opportunities for undervalued assets, leading to long-term gains.
4. Options Trading Becomes More Expensive but Rewarding
Higher volatility increases options premiums, making them more expensive to buy. However, options traders can also benefit from strategies like straddles and strangles, which profit from large price swings in either direction.
5. Stop-Loss Strategies Need Adjustment
In volatile markets, traders often widen stop-loss levels to avoid getting stopped out by temporary price swings. However, this requires careful planning to balance risk and prevent excessive losses.
6. Hedging Becomes More Crucial
Investors use hedging techniques, such as buying inverse ETFs or options, to protect their portfolios from downside risks in volatile markets. This helps in reducing potential losses while maintaining exposure to long-term gains.
7. Market Timing Becomes More Challenging
High volatility makes it harder to predict market trends, increasing the risk of entering or exiting trades at the wrong time. Traders must rely more on technical indicators, trend analysis, and news monitoring to make informed decisions.
Strategies for Trading in Volatile Markets
Trading in volatile markets requires a well-planned approach to manage risk while taking advantage of price fluctuations. High volatility can present opportunities for quick profits, but it also increases the likelihood of losses if not handled properly. Traders must use disciplined strategies to navigate unpredictable market conditions effectively. Below are some essential strategies to help traders succeed in volatile markets.
Key Strategies for Trading in Volatile Markets:
- Use Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Setting predefined exit points helps limit losses and secure profits before the market reverses unexpectedly.
- Trade with Reduced Position Sizes: Lowering trade sizes minimizes exposure to extreme price swings, reducing the risk of large losses.
- Focus on High-Quality Stocks or Assets: Investing in fundamentally strong assets can provide stability, as these tend to recover faster from market fluctuations.
- Utilize Hedging Strategies: Using options, inverse ETFs, or diversification techniques can help mitigate risks during volatile conditions.
- Monitor Market News and Events Closely: Staying updated on economic reports, interest rate decisions, and geopolitical events helps anticipate market movements.
- Adjust Trading Timeframes: Shortening trading timeframes can help traders react quickly to price changes, while long-term investors may find opportunities in market dips.
- Use Technical Indicators for Better Entry and Exit Points: Tools like Bollinger Bands, RSI, and moving averages can help identify overbought or oversold conditions, improving trade accuracy.
- Stay Emotionally Disciplined: Avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed, as emotional trading often leads to costly mistakes in volatile markets.
 Pros and Cons of Market Volatility
Pros and Cons of Market Volatility
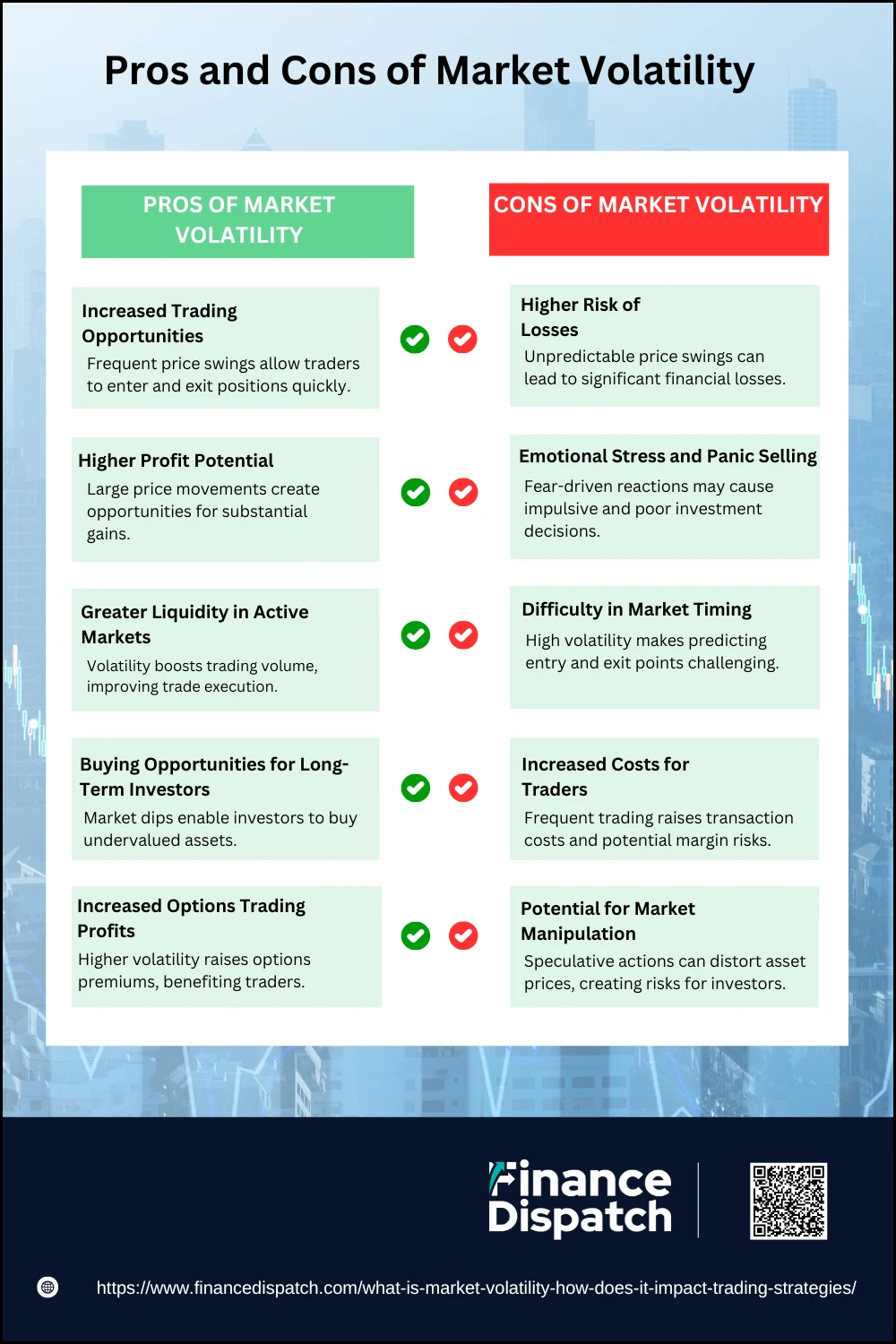
Market volatility is an inherent characteristic of financial markets that reflects the degree of price fluctuations in assets over a given period. It can be triggered by economic events, investor sentiment, political developments, or global crises. While some traders and investors view volatility as an opportunity to make substantial profits, others see it as a risk that can lead to significant losses. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of volatility is crucial for developing a well-balanced trading approach. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key pros and cons of market volatility.
Pros of Market Volatility:
1. Increased Trading Opportunities
When markets are volatile, prices fluctuate frequently, creating multiple opportunities for traders to enter and exit positions. This is especially beneficial for short-term traders like day traders and swing traders who capitalize on rapid price movements.
2. Higher Profit Potential
Large price swings in volatile markets provide greater profit potential. Skilled traders who can correctly predict market movements can generate significant returns in a short period, making volatility an attractive aspect of trading.
3. Greater Liquidity in Active Markets
Volatility often increases trading volume, making markets more liquid. Higher liquidity means traders can buy and sell assets more easily without experiencing significant price slippage, ensuring smoother trade execution.
4. Buying Opportunities for Long-Term Investors
Periods of market volatility often lead to sharp declines in asset prices, sometimes undervaluing strong companies or investments. Long-term investors can take advantage of these downturns by purchasing high-quality stocks at discounted prices and benefiting from future growth.
5. Increased Options Trading Profits
In volatile markets, options premiums tend to rise due to greater uncertainty about future price movements. This benefits options traders who employ strategies like straddles, strangles, or volatility-based trading methods to capitalize on price swings.
Cons of Market Volatility:
1. Higher Risk of Losses
The rapid and unpredictable nature of volatile markets can lead to significant losses, especially for inexperienced traders who may struggle to manage risk effectively. Without proper stop-loss strategies, traders may face unexpected and substantial financial setbacks.
2. Emotional Stress and Panic Selling
Market volatility can trigger emotional reactions such as fear and greed, leading to impulsive decisions. Many investors panic when markets drop sharply, selling assets at a loss instead of holding onto fundamentally strong investments for the long term.
3. Difficulty in Market Timing
High volatility makes it harder to predict price trends, increasing the risk of entering or exiting trades at the wrong time. Even experienced traders find it challenging to determine the best moments to buy or sell in highly volatile conditions.
4. Increased Costs for Traders
Active trading in volatile markets often leads to higher transaction costs, including brokerage commissions, spreads, and slippage. Additionally, traders using margin or leveraged positions may face margin calls if prices move sharply against them.
5. Potential for Market Manipulation
Extremely volatile markets can sometimes be influenced by speculative traders, algorithmic trading, or misleading information. Pump-and-dump schemes, short squeezes, and other manipulative tactics can drive asset prices in unsustainable directions, creating additional risks for retail investors.
Trading Strategies for Different Volatility Levels
Market volatility can vary significantly, ranging from periods of high price swings to relatively stable market conditions. Traders need to adjust their strategies based on the level of volatility to maximize profits while minimizing risks. High volatility offers more trading opportunities but comes with increased uncertainty, whereas low volatility provides stability but may limit profit potential. Understanding how to adapt trading strategies to different market conditions is crucial for long-term success. Below are key trading strategies for different volatility levels.
Strategies for High Volatility Markets:
- Use Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Set wider stop-loss levels to avoid being stopped out by temporary price swings, while take-profit orders can help lock in gains before the market reverses.
- Trade in Shorter Timeframes: High volatility favors day traders and scalpers who can capitalize on rapid price movements within minutes or hours.
- Consider Options Strategies: Strategies like straddles and strangles allow traders to profit from large price swings, regardless of the direction.
- Diversify to Reduce Risk: Holding a mix of assets, including defensive stocks or bonds, can help offset losses during extreme market swings.
- Avoid Overleveraging: Using too much leverage in volatile conditions can lead to large losses if the market moves against your position.
Strategies for Low Volatility Markets:
- Focus on Trend-Following Strategies: When the market is stable, traders can use moving averages and momentum indicators to follow long-term trends.
- Use Range Trading: Identify support and resistance levels and trade within the established range, buying near support and selling near resistance.
- Sell Options for Premiums: Low volatility reduces options prices, making it a good time to sell covered calls or cash-secured puts for steady income.
- Increase Position Sizes Gradually: Since price movements are smaller, traders may need to slightly increase their trade sizes while maintaining risk control.
- Wait for Breakout Confirmation: In low-volatility markets, price consolidations often lead to breakouts. Wait for confirmation before entering a trade to avoid false signals.
Conclusion
Market volatility is a crucial factor that influences trading strategies, risk management, and overall market behavior. Whether dealing with high or low volatility, traders must adapt their approaches to align with prevailing market conditions. High volatility presents opportunities for rapid gains but requires strict risk controls, while low volatility offers stability but demands patience and trend-following strategies. Understanding different volatility levels and implementing appropriate trading techniques can help traders navigate market fluctuations more effectively. By staying informed, using proper risk management tools, and adjusting strategies as needed, traders can enhance their chances of success in any market environment.