A cold wallet is a cryptocurrency storage solution that keeps your private keys offline, offering unmatched security against online threats like hacking and malware. These wallets are designed to store private keys, which are the cryptographic codes granting access to your digital assets, in an environment that never connects to the internet. This makes cold wallets an ideal choice for long-term storage of significant cryptocurrency holdings or for those who prioritize the security of their investments. Unlike hot wallets, which are online and convenient for frequent transactions, cold wallets focus on protection by eliminating the risks associated with internet connectivity. Common types of cold wallets include hardware wallets, paper wallets, and even more unconventional methods like sound wallets or deep cold storage solutions. By keeping your keys offline, cold wallets ensure your assets remain safe from the vulnerabilities of the digital world.

Why Do You Need a Cold Wallet?
A cold wallet is essential for anyone looking to safeguard their cryptocurrency holdings against online threats. Unlike traditional bank accounts, cryptocurrencies do not have institutional backing or insurance, meaning any loss due to hacking or theft is irreversible. Cold wallets provide a secure, offline storage solution that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, giving you full control over your assets and peace of mind.
1. Protection Against Cyber Threats
Cold wallets provide unmatched security by keeping your private keys completely offline. This isolation ensures they are not exposed to risks like hacking, phishing, or malware, which frequently target hot wallets or exchange platforms. Cybercriminals cannot access private keys stored in a cold wallet, even if your computer or smartphone is compromised. This makes cold wallets a crucial defense mechanism for safeguarding your cryptocurrency from the ever-evolving tactics of cyber attackers.
2. Control Over Your Assets
When using a cold wallet, you retain full ownership of your private keys, which means you have ultimate control over your cryptocurrency. Unlike custodial wallets or exchange platforms that hold your keys on your behalf, a cold wallet ensures no third party can freeze, access, or mismanage your funds. The popular crypto adage, “Not your keys, not your coins,” highlights the importance of self-custody, and cold wallets empower you to take full responsibility for your digital assets.
3. Secure Long-Term Storage
Cold wallets are the ideal choice for long-term cryptocurrency storage. They are designed to protect significant holdings over extended periods without the need for regular access or monitoring. Whether you’re holding Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other digital assets as a long-term investment, a cold wallet minimizes the chances of theft or accidental loss, giving you the confidence to HODL (Hold On for Dear Life) securely.
4. Defense Against Smart Contract Risks
One of the lesser-known benefits of cold wallets is their immunity to on-chain threats like malicious smart contracts. Many blockchain applications and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms require users to grant permissions for transactions, which can sometimes be exploited. Cold wallets do not connect to the internet or interact with smart contracts, effectively removing the risk of falling victim to malicious approvals or fraudulent applications.
5. Reduced Dependency on Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges, while convenient for trading, are frequent targets for hackers. Keeping your assets in an exchange wallet exposes you to the risk of exchange breaches, freezes, or insolvency. By transferring your holdings to a cold wallet, you eliminate dependency on these platforms and ensure your funds remain safe, regardless of the exchange’s operational security or financial stability.
6. Versatility in Storage Options
Cold wallets come in various forms, offering flexibility to meet different preferences and technical abilities. Hardware wallets, like Ledger or Trezor, provide robust security with user-friendly interfaces, while paper wallets allow for low-tech offline storage. Advanced users might explore sound wallets or deep cold storage methods for added layers of protection. This variety allows you to choose the storage solution that best fits your needs, ensuring you feel comfortable and confident managing your assets.

Types of Cold Wallets
Cold wallets come in various forms, each designed to keep your cryptocurrency private keys secure by storing them offline. The different types cater to diverse needs, ranging from high-tech solutions to simple, cost-effective methods. Understanding these options can help you choose the right cold wallet to match your security and usability preferences.
1. Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed specifically to store private keys securely. These wallets, such as Ledger or Trezor, generate keys offline and allow users to sign transactions without exposing the keys to the internet. With features like PIN protection and secure element chips, they are among the most secure and user-friendly cold storage solutions.
2. Paper Wallets
A paper wallet involves writing or printing your private and public keys on a physical piece of paper. This is one of the simplest and most affordable forms of cold storage. While it ensures the keys remain offline, paper wallets are susceptible to physical damage, theft, or loss, making secure storage a critical consideration.
3. Metal Wallets
Metal wallets serve as a durable alternative to paper wallets. These are physical plates made from materials like stainless steel, engraved with your private key or seed phrase. They are resistant to fire, water, and other environmental hazards, providing a long-lasting solution for securely storing your keys.
4. Sound Wallets
A sound wallet stores private keys in an encrypted audio file, which can be saved on devices like CDs or USB drives. While innovative, sound wallets are less common due to their complexity and the need for specialized tools to decode the keys. They provide an unconventional but effective method of keeping keys offline.
5. Offline Software Wallets
Offline software wallets involve using a computer that is never connected to the internet to generate and store private keys. Transactions are signed on the offline device and then transferred to an online device for broadcasting. This method offers strong security but requires a high level of technical expertise to set up and maintain.
6. Brain Wallets
Brain wallets rely on memorizing your private key or seed phrase, rather than storing it physically. While this method eliminates physical risks, it requires a strong memory and the ability to recall complex phrases without error. Forgetting the phrase results in permanent loss of access to your funds.
7. Deep Cold Storage
Deep cold storage refers to storing private keys in highly secure, often inconvenient-to-access locations. This could involve placing a hardware wallet in a safety deposit box, burying it in a waterproof container, or using a third-party vault service. While extremely secure, deep cold storage can be less practical for frequent access.

How Does a Cold Wallet Work?
Cold wallet works as follows:
1. Key Generation in an Offline Environment
The first step in using a cold wallet is generating a pair of cryptographic keys—a public key for receiving cryptocurrency and a private key for accessing it. This process occurs in a completely offline environment, such as a hardware wallet, an air-gapped computer, or a secure offline app. By keeping the key generation offline, cold wallets eliminate the possibility of online threats, like malware or phishing attacks, capturing the private key during its creation.
2. Secure Private Key Storage
Once the private key is generated, it is stored securely in the cold wallet. Depending on the type of cold wallet, this might be a hardware device, a piece of paper, a metal plate, or even an audio file in the case of sound wallets. This offline storage ensures that the private key remains inaccessible to hackers or malicious software, providing robust protection for your cryptocurrency.
3. Transaction Creation on an Online Device
When you need to send cryptocurrency, the transaction begins on an online device, such as a smartphone or computer. You specify details like the recipient’s wallet address and the amount to be transferred. This transaction remains unsigned at this stage, ensuring that the private key, which is stored offline, is not yet involved.
4. Offline Transaction Signing
The unsigned transaction is transferred to the cold wallet, which signs it using the stored private key. This signing process happens entirely offline, ensuring that the private key is never exposed to the internet. Depending on the type of cold wallet, the transaction may be transferred via USB, QR code, or other secure methods.
5. Broadcasting the Signed Transaction
After the transaction is signed, it is moved back to the online device and broadcasted to the blockchain network. The signed transaction contains the necessary authorization for the transfer, without exposing the private key. This separation of signing and broadcasting ensures that your keys remain secure while enabling you to complete transactions.
6. Backup and Recovery Options
Cold wallets offer recovery mechanisms, like seed phrases, which act as a backup for your private key. If the physical wallet is lost, stolen, or damaged, you can use the seed phrase to restore access to your funds on a new device. These recovery options ensure you don’t lose access to your cryptocurrency due to unforeseen circumstances, but they must be stored securely to prevent misuse.

Differences Between a Cold Wallet and a Hot Wallet
Cold wallets and hot wallets are both essential tools for storing and managing cryptocurrency, but they differ significantly in terms of security, accessibility, and usability. Understanding the differences between the two can help you choose the right solution based on your needs.
| Feature | Cold Wallet | Hot Wallet |
| Storage Environment | Offline | Online |
| Security | Highly secure; immune to online hacking | Vulnerable to online threats like phishing, malware, and hacking |
| Accessibility | Limited; requires additional steps to access | Easily accessible for frequent transactions |
| Best Use Case | Long-term storage of large cryptocurrency holdings | Day-to-day transactions and frequent trading |
| Examples | Hardware wallets, paper wallets, metal wallets | Exchange wallets, mobile wallets, browser-based wallets |
| Cost | Often comes with an upfront cost (e.g., hardware wallets) | Many are free to use |
| Technical Knowledge Required | Moderate; setup and usage may require learning | Low; generally user-friendly and easy to operate |
| Risk of Theft | Low; physical theft or loss is the main risk | High; prone to hacking and unauthorized access |
| Recovery Options | Seed phrases or backups needed for recovery | Usually recoverable through exchange support or app features |
| Transaction Speed | Slower due to the offline signing process | Faster; transactions can be signed instantly |
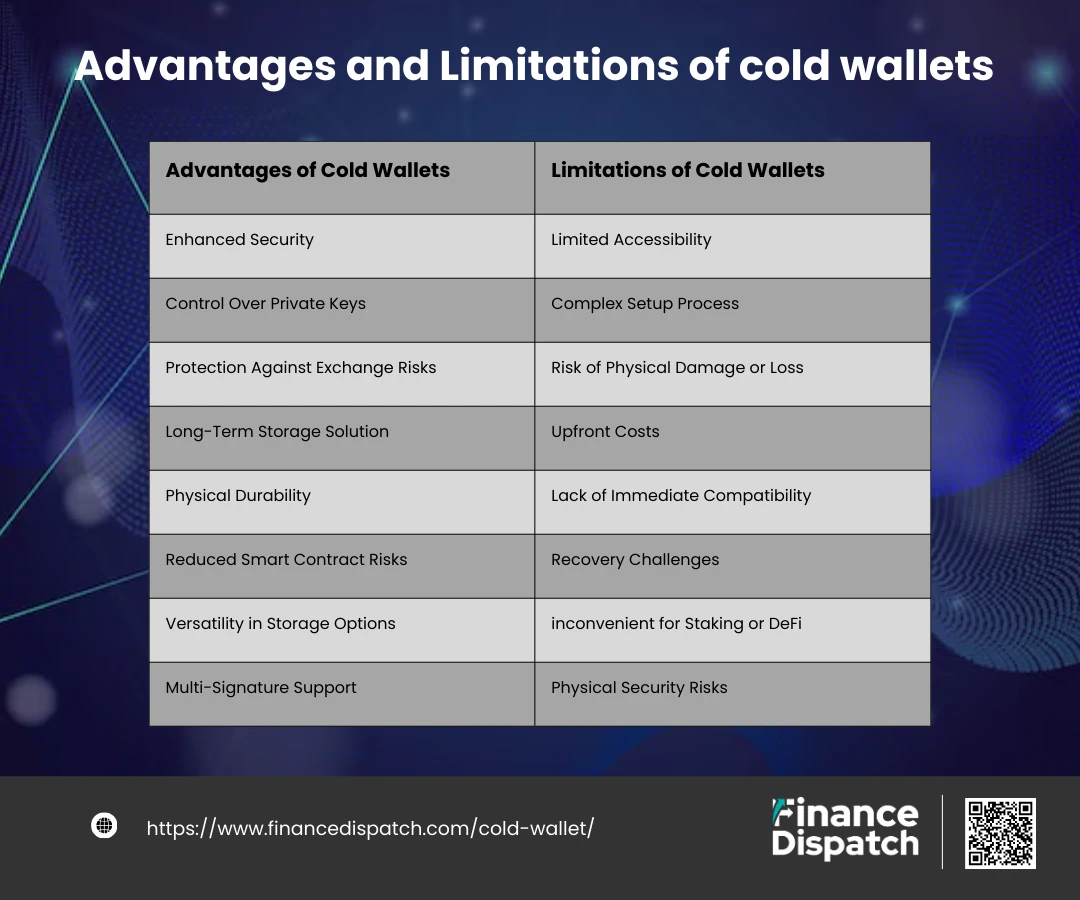
Advantages of Cold Wallets
Cold wallets offer unparalleled security for cryptocurrency storage, making them a top choice for investors who prioritize asset safety. Here are some advantages of Cold Wallets:
1. Enhanced Security
The primary advantage of cold wallets is their ability to keep private keys offline, completely removing exposure to online threats like hacking, phishing, and malware. This offline, air-gapped environment ensures that even if your internet-connected device is compromised, your cryptocurrency remains secure. For investors prioritizing security, cold wallets are an unmatched solution.
2. Control Over Private Keys
With cold wallets, you are the sole custodian of your private keys. Unlike custodial solutions, such as exchange wallets, no third party has access to your keys, giving you full ownership of and responsibility for your cryptocurrency. This autonomy means your funds cannot be frozen, mismanaged, or accessed without your consent.
3. Protection Against Exchange Risks
Cryptocurrencies stored on exchanges are vulnerable to platform hacks, system outages, or even the financial collapse of the exchange itself. Cold wallets eliminate reliance on these platforms, ensuring that your funds remain safe regardless of external events affecting the exchange.
4. Long-Term Storage Solution
Cold wallets are specifically designed for long-term storage, making them ideal for users who intend to hold (HODL) large amounts of cryptocurrency without frequent transactions. Their robust security features and durability ensure that your assets remain protected for years, even decades.
5. Physical Durability
Many cold wallets, such as hardware and metal wallets, are built to withstand environmental hazards. Metal wallets, for instance, are resistant to fire, water, and general wear, ensuring your private keys remain intact in extreme conditions. This physical durability makes them a dependable choice for safeguarding your recovery information.
6. Reduced Smart Contract Risks
Cold wallets do not interact with blockchain applications or smart contracts, which eliminates the risk of malicious contract approvals. This isolation protects your assets from common on-chain threats, including exploitative decentralized apps or fraudulent smart contract transactions.
7. Versatility in Storage Options
Cold wallets cater to a variety of preferences and technical expertise. Hardware wallets are user-friendly and secure, while paper wallets and metal backups provide cost-effective alternatives. This flexibility allows users to choose a storage method that best suits their needs, from simple solutions to more advanced setups.
8. Multi-Signature Support
Some cold wallets support multi-signature functionality, requiring multiple keys to authorize a transaction. This feature adds an extra layer of protection by distributing access among multiple parties or devices, making unauthorized transactions significantly more difficult. It’s especially useful for businesses or individuals managing large cryptocurrency holdings.
Limitations of Cold Wallets
While cold wallets are highly secure for storing cryptocurrency, they are not without limitations. Their offline nature and additional layers of protection can sometimes come at the cost of convenience, accessibility, and usability. Understanding these limitations is essential for making an informed decision about whether a cold wallet suits your needs.
1. Limited Accessibility
Cold wallets are not ideal for frequent or immediate transactions due to their offline nature. For example, accessing funds stored on a hardware wallet requires physically connecting the device to a computer or smartphone and using companion software. Similarly, using a paper wallet involves importing keys into a hot wallet to make a transaction, temporarily exposing them to online risks. This makes cold wallets less convenient for users who regularly trade or make payments.
2. Complex Setup Process
Setting up a cold wallet can be a daunting task for beginners. The process involves generating private keys, writing down recovery phrases, and configuring the device or method securely. Any mistake during setup, such as exposing the private key online or mishandling the seed phrase, can compromise security or lead to the loss of funds. This complexity may discourage less tech-savvy users from adopting cold wallets.
3. Risk of Physical Damage or Loss
Cold wallets are susceptible to physical hazards. Paper wallets can be destroyed by fire, water, or general wear and tear, while hardware wallets can be damaged, stolen, or misplaced. Without proper backups, losing or damaging a cold wallet could mean losing access to your cryptocurrency permanently.
4. Upfront Costs
Many cold wallets, particularly hardware wallets, require an upfront investment, with prices ranging from $50 to $200 or more. For users with smaller cryptocurrency holdings, the cost of a hardware wallet may outweigh its benefits. This makes cold wallets less accessible for individuals looking for low-cost storage solutions.
5. Lack of Immediate Compatibility
Cold wallets may not support all cryptocurrencies or blockchain networks. While major coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum are typically supported, lesser-known tokens might require additional configuration or may not be supported at all. Adding support for new tokens often requires firmware updates or other technical adjustments, limiting the wallet’s flexibility for diversified portfolios.
6. Recovery Challenges
Recovering funds from a cold wallet depends entirely on the safe storage of recovery phrases or seed backups. Losing this information could result in permanent loss of your cryptocurrency. Additionally, mishandling recovery phrases—such as storing them in insecure locations—can expose your assets to theft or unauthorized access.
7. Inconvenient for Staking or DeFi
Cold wallets are designed for static storage, making them unsuitable for activities that require active interaction with the blockchain, such as staking, liquidity provision, or engaging with decentralized applications (Apps). Users often need to transfer funds to a hot wallet for these activities, introducing extra steps and potential exposure to risks during the transfer process.
8. Physical Security Risks
While cold wallets are immune to online threats, they can be stolen or accessed by unauthorized individuals. For instance, a lost or stolen hardware wallet can be used by someone who discovers the PIN or recovery phrase. Proper physical storage, such as safes or safety deposit boxes, is necessary to mitigate these risks.
9. Technical Knowledge Required
Cold wallets demand a higher level of technical understanding compared to hot wallets. Users must know how to sign transactions offline, manage private keys, and safeguard recovery phrases. Additionally, troubleshooting issues like firmware updates or compatibility problems may require advanced skills, which can be a barrier for less experienced users.
Can a Cold Wallet Be Hacked?
A cold wallet is designed to be one of the most secure methods for storing cryptocurrency because it keeps private keys completely offline, making them immune to online threats like hacking, phishing, or malware. However, no system is entirely invulnerable. Cold wallets can be hacked indirectly if users mishandle their recovery phrases, expose their private keys during setup or use, or fall victim to physical theft of the wallet itself. Advanced physical attacks, such as tampering with the hardware or exploiting side-channel vulnerabilities in hardware wallets, are rare but possible. Additionally, if a recovery phrase is stored insecurely or shared with untrusted parties, an attacker could gain access to the funds. While the chances of hacking are drastically reduced with a cold wallet compared to a hot wallet, maintaining strong physical security, proper backups, and secure handling practices is essential to ensure complete protection.
How to Create and Transfer Crypto to a Cold Wallet
Creating a cold wallet and transferring cryptocurrency to it is a straightforward process that requires careful attention to detail to ensure security. By setting up a cold wallet correctly and transferring funds securely, you can protect your digital assets from online threats and enjoy peace of mind. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
1. Choose Your Cold Wallet Type
Selecting the right cold wallet is crucial for ensuring your cryptocurrency’s security and your comfort with managing it. Hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor are user-friendly and highly secure, while paper wallets are a low-cost option suitable for those with a good understanding of offline key management. Offline software wallets, which require an air-gapped computer, offer robust security but demand more technical expertise. Consider factors like the value of your holdings, how often you need access, and your budget to choose the best option.
2. Purchase or Prepare the Wallet
If you opt for a hardware wallet, ensure you purchase it from a trusted vendor or directly from the manufacturer to avoid tampered or counterfeit devices. For paper wallets, use a trusted, open-source, offline key generator, and for software wallets, prepare a computer that has never been connected to the internet. This step minimizes exposure to potential risks during wallet creation.
3. Set Up the Wallet
Hardware wallets come with step-by-step instructions from the manufacturer. Follow these carefully to generate your private keys securely. Paper wallets require printing or writing down your keys after generating them offline. Software wallets often involve installing the application on an air-gapped computer. In all cases, the setup process will generate a recovery phrase or private key. Store this information securely, as it is the only way to recover your funds if the wallet is lost or damaged.
4. Generate a Receiving Address
After completing the setup, generate a public address to receive cryptocurrency. For hardware wallets, this is done through the companion software or app, while paper wallets display the public key directly. Offline software wallets allow you to generate multiple addresses, which can be used for different transactions. Ensure the address you generate matches the cryptocurrency you intend to transfer.
5. Access Your Current Wallet or Exchange
Log in to your existing hot wallet or cryptocurrency exchange where your funds are stored. Confirm that the platform supports withdrawals to external wallets and that your account is secure, with two-factor authentication enabled if possible.
6. Initiate the Transfer
Copy the public receiving address from your cold wallet and paste it into the “Send” or “Withdraw” field on your current wallet or exchange. Double-check the address, as cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible. If you accidentally send funds to the wrong address, they cannot be recovered.
7. Confirm the Transfer
Specify the amount of cryptocurrency you want to transfer and confirm the transaction. Depending on the platform, you may need to enter additional security credentials, such as a one-time password or verification code. Once confirmed, the transaction will be processed and sent to the blockchain for verification.
8. Verify the Transaction
Use a blockchain explorer to track and confirm the transaction. Enter the public receiving address or transaction ID to ensure the funds have arrived safely in your cold wallet. This step provides peace of mind and confirms the accuracy of the transfer.
9. Disconnect and Store the Wallet Safely
After confirming the transfer, disconnect the hardware wallet from your computer or secure the paper/software wallet. Store the wallet and recovery phrase in a secure location, such as a fireproof safe or safety deposit box. This ensures that your funds are protected from physical theft, damage, or loss.
Popular Cold Wallets
Popular cold wallets are trusted tools for securely storing cryptocurrency offline. Each wallet offers unique features, catering to different needs and preferences. From hardware wallets to alternative solutions like paper or metal wallets, these options provide robust security for long-term storage. Here’s a list of some of the most popular and reliable cold wallets available today.
Popular Cold Wallets:
1. Ledger Nano X
The Ledger Nano X is a leading hardware wallet known for its strong security features and Bluetooth connectivity, allowing wireless access. It supports over 1,800 cryptocurrencies and provides a seamless user experience through its companion app, Ledger Live. Its secure element chip ensures private keys remain protected.
2. Trezor Model T
Trezor Model T offers advanced security with a touchscreen interface for user-friendly operation. Supporting multiple cryptocurrencies, it’s ideal for those managing diverse portfolios. Open-source software and multi-signature support add to its appeal for advanced users.
3. Ledger Nano S Plus
A more affordable option from Ledger, the Nano S Plus provides the same robust security as the Nano X but without Bluetooth connectivity. It’s perfect for users who prioritize security and don’t need mobile access.
4. Coldcard Wallet
The Coldcard Wallet is designed specifically for Bitcoin users, offering top-notch security features like PIN protection and offline transaction signing. Its open-source firmware and Bitcoin-only focus make it a favorite among Bitcoin enthusiasts.
5. Paper Wallets
Paper wallets are a simple, low-cost cold storage option. By printing private keys or seed phrases on paper, users can store their cryptocurrency offline. However, they require careful handling to avoid physical damage or loss.
6. Metal Wallets (e.g., Cryptosteel or Billfodl)
Metal wallets are durable alternatives to paper wallets, designed to store recovery phrases or private keys engraved on metal plates. They are resistant to fire, water, and wear, making them a reliable option for long-term storage.
7. Trezor Model One
A more budget-friendly version of the Trezor Model T, the Model One provides essential security features for beginners or those with smaller cryptocurrency holdings. It supports fewer coins than the Model T but remains a reliable entry-level option.
8. Ellipal Titan
The Ellipal Titan is a hardware wallet with air-gapped security, meaning it never connects via USB or Bluetooth. It uses QR codes for transactions, adding an extra layer of protection. Its rugged, tamper-proof design is ideal for users who prioritize physical security.
9. BitBox02
The BitBox02 hardware wallet is compact and simple to use, offering robust security features. It supports multiple cryptocurrencies and includes a microSD card for backups, ensuring easy recovery.
10. KeepKey
KeepKey is a sleek and user-friendly hardware wallet supporting popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Its large screen makes transaction verification easy, and it integrates well with ShapeShift for convenient asset management.
Conclusion
Cold wallets are an indispensable tool for anyone serious about safeguarding their cryptocurrency investments. By storing private keys offline, they provide unparalleled protection against online threats such as hacking, phishing, and malware. Whether you opt for a hardware wallet, paper wallet, or another form of cold storage, the key is to choose a solution that aligns with your security needs and technical expertise. While cold wallets have limitations, such as accessibility and setup complexity, adhering to best practices ensures your digital assets remain safe for the long term. As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, a well-secured cold wallet will remain a cornerstone of responsible and effective crypto management.
FAQs
1. Can a Cold Wallet Be Used for Multiple Cryptocurrencies?
Yes, most modern cold wallets, such as hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor, support multiple cryptocurrencies. However, the range of supported coins depends on the wallet model and its compatibility with specific blockchain networks. Always check the list of supported assets before purchasing a cold wallet to ensure it meets your needs.
2. What Happens If My Cold Wallet Gets Stolen?
If your cold wallet is stolen, your funds remain secure as long as the thief does not have access to your PIN or recovery phrase. Hardware wallets are designed to lock or reset after multiple incorrect PIN attempts. If you suspect theft, you can use your recovery phrase to transfer your assets to a new wallet, rendering the stolen wallet useless.
3. Is It Safe to Buy a Second-Hand Hardware Wallet?
No, it is not recommended to buy second-hand hardware wallets. Pre-owned wallets could have been tampered with or compromised by malicious actors. Always purchase hardware wallets directly from the manufacturer or a trusted retailer to ensure the device is secure and has not been altered.
4. Can I Use a Cold Wallet Without an Internet Connection?
Yes, cold wallets are specifically designed for offline use. For transactions, the signing process occurs offline within the wallet, and only the signed transaction data is transferred to an internet-connected device to broadcast it to the blockchain. This ensures that private keys are never exposed to online threats.
5. How Often Should I Update My Hardware Wallet’s Firmware?
Firmware updates are essential for maintaining security and ensuring compatibility with the latest cryptocurrencies. You should check for updates regularly, ideally once every few months, or whenever the manufacturer announces a new update. Always download updates directly from the official website to avoid counterfeit software.